Tinea cruris, most commonly known as jock itch, is a fungal infection of the skin.
It belongs to a group of fungal skin infections called tinea. Like other tinea infections, jock itch is caused by mold-like fungi, which are known as dermatophytes. These microscopic fungi live on the skin as well as on the hair and nails.
They’re typically harmless, but they can multiply quickly and cause infections when they’re allowed to thrive in warm, moist areas. That’s why jock itch usually develops in the skin around the groin, inner thighs, and buttocks.
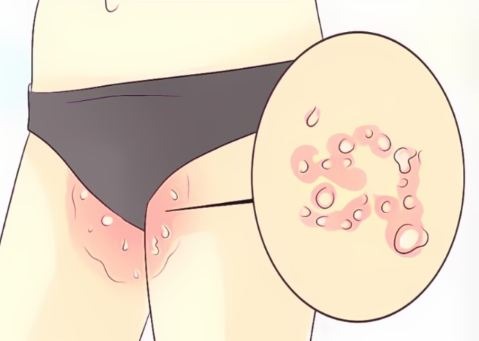
Jock itch is most common in men and adolescent boys. The infection causes a rash that often itches or burns. The affected areas can also be red, flaky, or scaly.
Though jock itch can be bothersome, it’s typically a mild infection. Treating it quickly will minimize symptoms and keep the infection from spreading.
Most people find relief simply by applying topical antifungal medications and by keeping the affected area clean and dry.
Common symptoms of jock itch in the affected area include:
- redness
- persistent itching
- burning sensation
- flaking, peeling, or cracking skin
- rash that gets worse with exercise or activity
- changes in skin color
- rash that doesn’t improve or worsens, or spreads with over-the-counter hydrocortisone (anti-itch) cream
Jock itch typically affects the groin and inner thighs. It may spread to the abdomen and buttocks, but the scrotum usually isn’t affected.
Jock itch is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes. These fungi naturally live on your skin and normally don’t cause problems. However, when you remain in sweat-soaked clothes after exercising, the lengthy exposure to moisture can allow the fungi to multiply quickly.
When you have an overgrowth of dermatophytes in your groin area, it causes the infection known as jock itch.
The fungus that causes jock itch is highly contagious. You may get the fungal infection through close personal contact with an infected person or through contact with the unwashed clothing of an infected person.
The term “jock itch” may give the impression that only athletes develop the infection, but it can happen to anyone. Those who are overweight are more likely to experience jock itch because the fungus can thrive in folds of skin, which are prone to sweating.
As a preventive measure, it’s important to wash with soap and water in your groin and armpit areas daily. Jock itch may also be triggered by prolonged exposure to moisture and friction from clothes.
Your doctor will likely be able to diagnose jock itch simply by performing a physical exam and inspecting the affected area of skin.
In some cases, your doctor may take some scrapings of skin cells from the area to help diagnose the condition. This may also help rule out other skin disorders, such as psoriasis.
In most cases, jock itch can be treated at home effectively. You can try the following remedies to get rid of the infection:
- Apply an over-the-counter antifungal cream, powder, or spray to the affected area.
- Wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and warm water.
- Dry the affected area thoroughly after bathing and exercise.
- Change clothes and undergarments every day.
- Wear loose cotton clothing.
- Treat any other fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot.
If your symptoms don’t improve after two weeks of home treatments, you should make an appointment to see your doctor. You may have developed a secondary infection that needs prompt treatment.
If you do have jock itch, but it’s not responding to over-the-counter medications and home remedies, your doctor may prescribe something stronger. Possible medications include:
- topical medications
- econazole (Ecoza)
- oxiconazole (Oxistat)
- oral medications
- itraconazole (Sporanox)
- fluconazole (Diflucan)
Oral antifungal medications may cause unpleasant side effects, such as upset stomach and headaches. If you experience any of these side effects, make sure to discuss them with your doctor.
Practicing good hygiene is the best defense against jock itch. Regular hand washing can greatly reduce your risk of getting this infection from someone else. It’s also important to keep your skin clean and dry, especially the area around your groin.
Wash the area regularly with soap, and dry the area thoroughly after bathing. Applying baby powder around your groin can also be helpful for preventing excess moisture.
Avoid tight-fitting clothing as that can further increase your risk of jock itch. Tight clothes can rub or chafe your skin, which makes you more susceptible. You may want to try wearing boxer shorts instead of boxer briefs.
It’s also beneficial to wear loose-fitting clothing in hot or humid weather. Loose clothing can prevent sweating and the warm, moist environment in which fungus thrives. Make sure you wash any workout clothes or athletic supporters after each use.
Athlete’s foot is another infection that can be caused by the same fungi that causes jock itch. If you have athlete’s foot, treat it quickly. You can avoid spreading it to your groin area by making sure you don’t use the same towel you use on your feet for your groin.
Q:
Will treatments for jock itch help with skin discoloration (or only the itch)?
A:
The treatment for jock itch will help eradicate the fungus that is causing the rash and also the symptoms of itchiness. However, the skin discoloration may not resolve fully in some people for weeks. In short, by treating the fungus, it allows that skin discoloration to resolve over time.

Thank you for useful information🤩🤩🤩
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
DeleteIt is our pleasure.
DeletePost a Comment